IoCs in Phishing Campaigns: A Focus on Support Chat Keys
March 21, 2024
Introduction
Phishing campaigns are a persistent threat to cybersecurity, with malicious actors constantly refining their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities. One emerging trend in these campaigns is the misuse of support chat keys, such as those provided by services like tawk.to and smartsuppchat.com. Initially designed to enhance customer support, these services can inadvertently become Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) when used maliciously.
Understanding IoCs
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) are artifacts observed in a network or system that indicate a security breach or intrusion has occurred. They can be as diverse as unusual network traffic patterns, suspicious IP addresses, or in this case, support chat keys embedded in phishing websites.
Support Chat Keys as IoCs
Support chat keys are unique identifiers used by chat services to connect users to the correct support team. In a phishing context, threat actors embed these keys into fake websites to create an illusion of legitimacy. These keys can serve as IoCs, helping cybersecurity professionals detect and respond to phishing attempts.
Tawk.to and smartsuppchat.com are popular chat services that provide free live chat widgets for websites. However, their popularity has also made them attractive tools for phishing campaigns.
Phishing websites can employ services like tawk.to or smartsuppchat.com to replicate the live chat function often found on legitimate sites. To enable chat and establish a connection to the intended support service, a webmaster must incorporate a JavaScript script containing specific public keys into their site. However, in a phishing context, these keys are not linked to the support service of a genuine organization but to a malicious team. The presence of a familiar support chat interface, similar to those found on reputable sites, can instill a false sense of trust in unsuspecting users. Moreover, as malicious actors have access to all messages from these chat rooms and may even respond, the possibility of users inadvertently divulging sensitive data to "support agents" cannot be discounted.
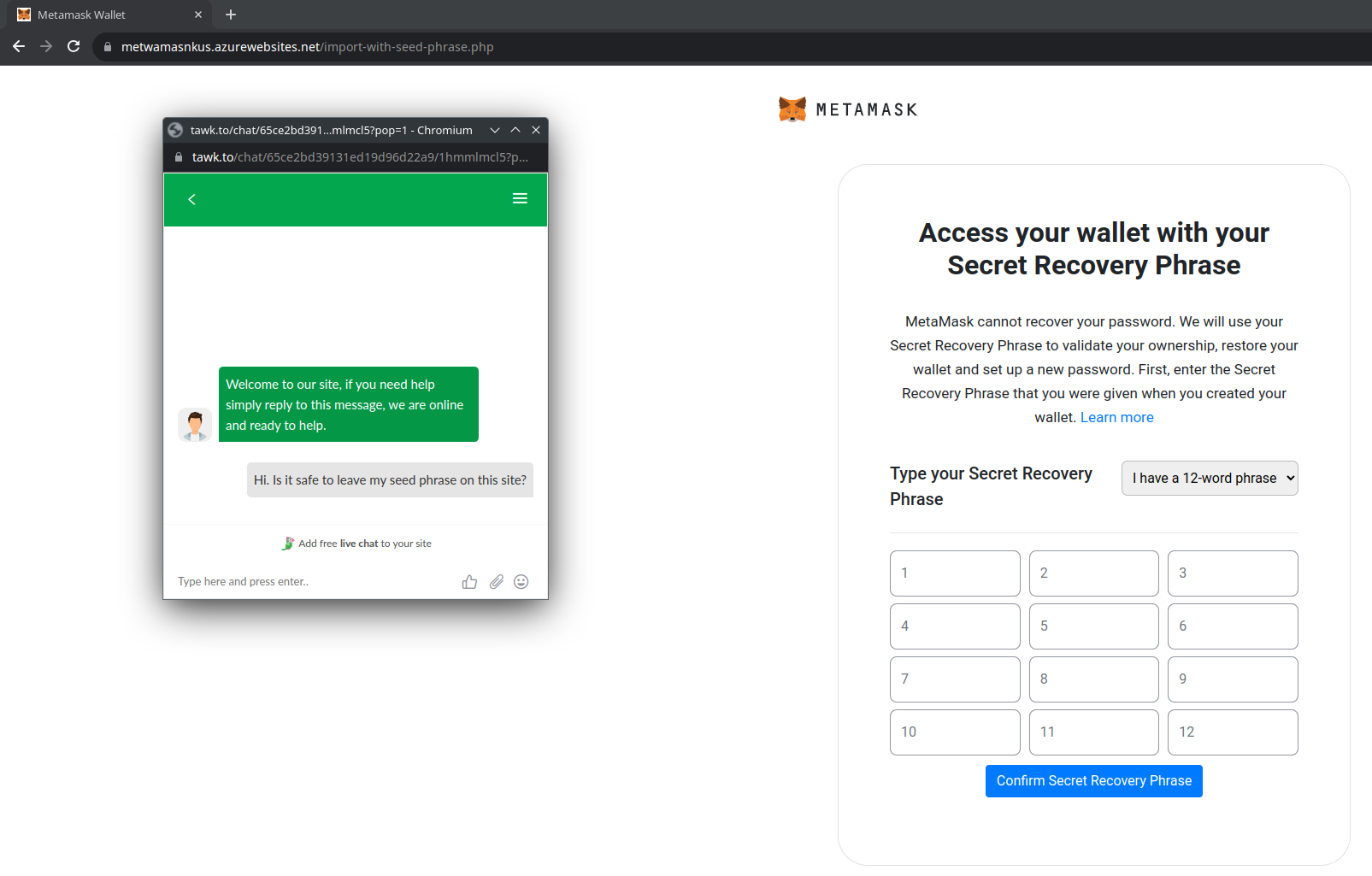
Detecting Such IoCs
The detection of such keys is relatively straightforward, as they are present both within the HTML code of a website and in HTTP requests. This dual presence facilitates their discovery, whether through static analysis of a site or dynamic analysis of network traffic.
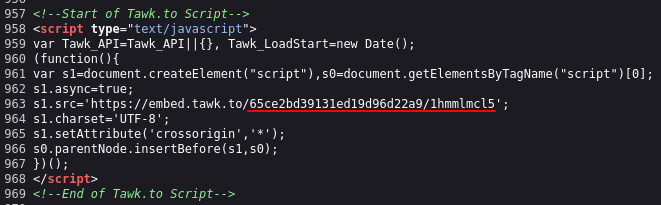
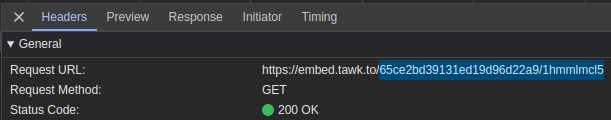
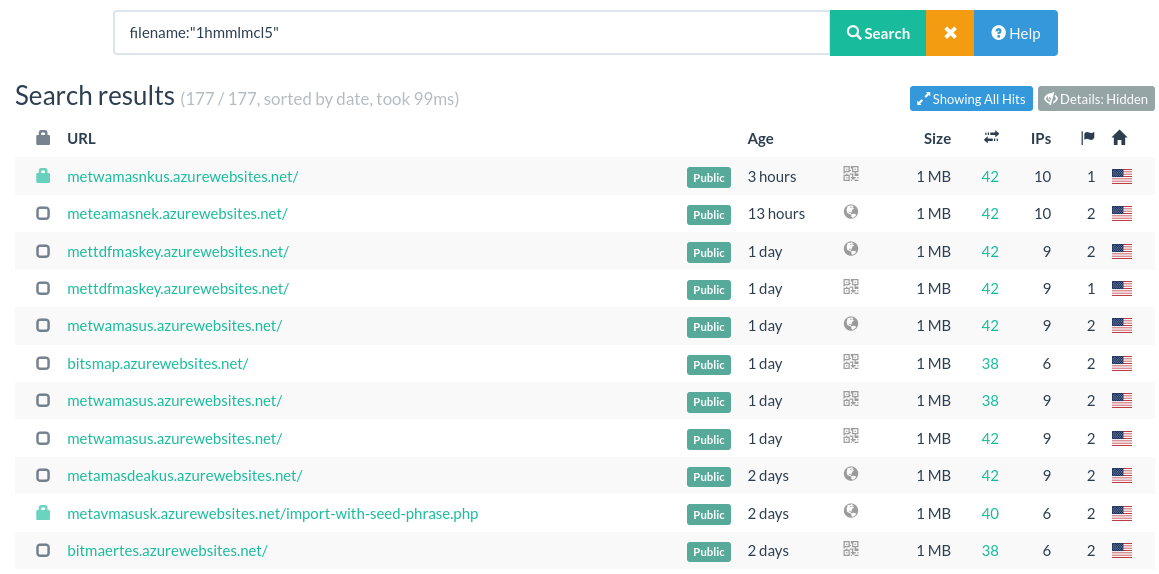
In the case of the malicious site hxxps://metwamasnkus.azurewebsites.net employs the tawk.to service with the unique key "65ce2bd39131ed19d96d22a9/1hmmlmcl5". By utilizing the urlscan.io service and conducting a search with the query "filename: 1hmmlmcl5", we were able to identify 177 pages hosted on various subdomains of azurewebsites.net, a domain owned by Microsoft Azure. Despite these pages featuring different templates, the presence of the same IoC suggests they are likely operated by the same threat actor. Without this IoC, associating these disparate sites would have been challenging. Furthermore, our investigation revealed phishing sites impersonating KuCoin, Bitstamp, Crypto.com, WalletConnect, Exodus Wallet, and Coinbase, all tied to the same IoC.
Responding to Such IoCs
Upon detection of malicious use of support chat keys, it is crucial to report the abuse to the respective chat service providers. Both tawk.to and smartsuppchat provide dedicated pages for reporting such misuse.
For tawk.to, the abuse reporting page can be found at https://www.tawk.to/legal/report-abuse/. This page provides a form where you can submit details about the abuse, including the unique key associated with the malicious site.
Similarly, smartsuppchat offers an abuse reporting page at https://help.smartsupp.com/en_US/report-scam. Here, you can report phishing or scam activities that misuse their service.
By reporting such abuses, you contribute to the collective effort of maintaining a safer digital environment. The service providers can then take necessary actions, such as disabling the malicious keys, preventing further misuse, and potentially assisting in the identification of the threat actors.
Conclusion
As phishing campaigns continue to evolve, so too must our approach to cybersecurity. By understanding how support chat keys can serve as IoCs, we can better detect and respond to these threats, protecting our data from potential compromise. It's a reminder that even the most innocuous-seeming features can be exploited, and vigilance is our best defense.